Beyond the Focus Group: Why Your Customers Can't Tell You What They Really Want
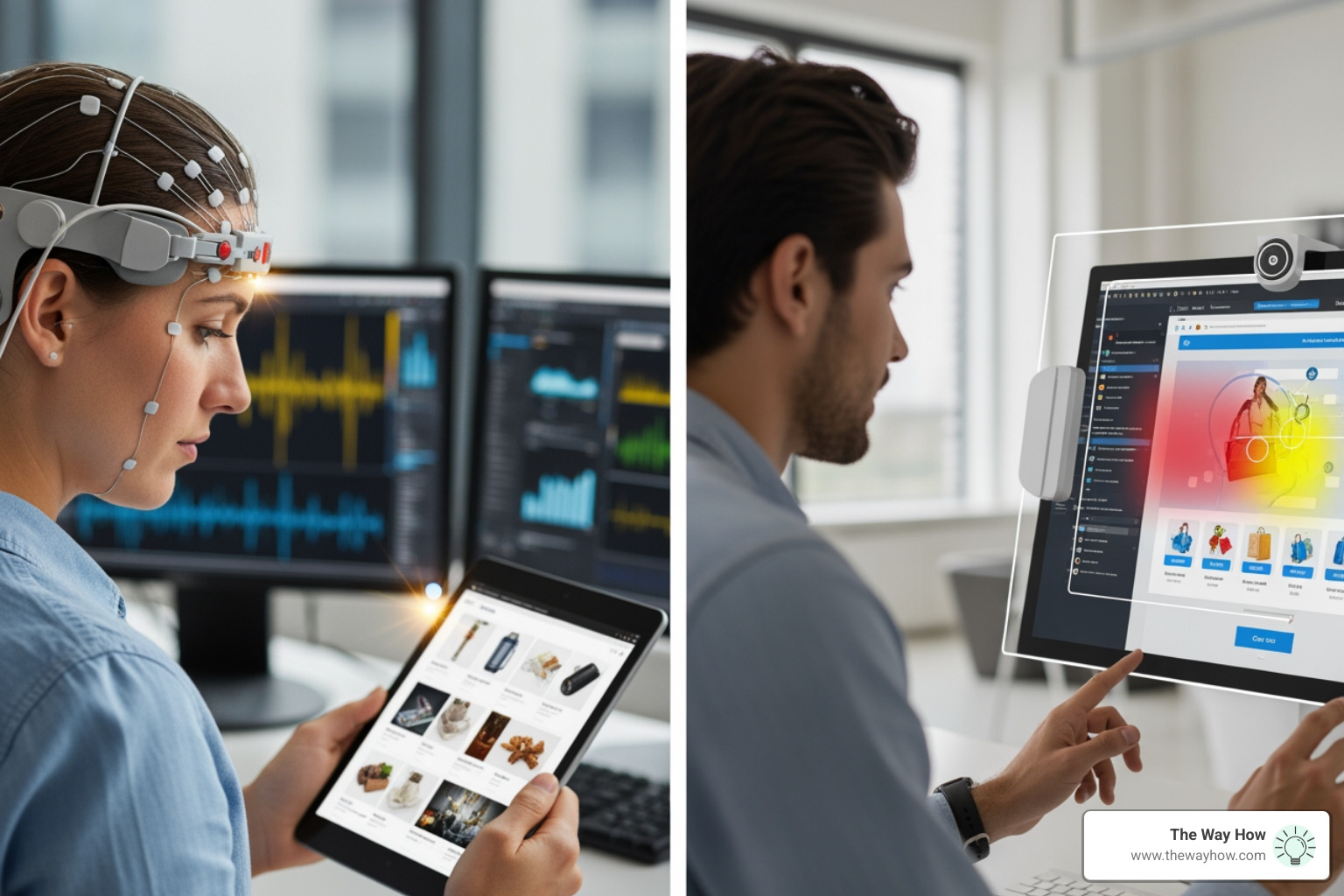
Neuromarketing techniques are scientific methods that use neuroscience tools—like brain imaging (fMRI, EEG), eye-tracking, facial coding, and biometric sensors—to measure subconscious consumer responses to marketing stimuli, revealing what people truly feel and think beyond what they consciously report.
The core neuromarketing techniques include:
- Brain Scanning (fMRI, EEG) — measures neural activity to understand attention, emotion, and memory
- Eye-Tracking — reveals where consumers look and what captures their attention
- Facial Coding — detects micro-expressions that signal emotional responses
- Biometric Measures (GSR, Heart Rate) — tracks physiological arousal and engagement
Here's what you already know: focus groups lie.
Not intentionally. But they do.
Ask someone what they'd pay for a product, and they'll anchor to what sounds reasonable. Ask them which ad they prefer, and they'll tell you the one that makes them feel smart for liking it. Ask them why they chose your brand, and they'll construct a narrative that has almost nothing to do with the neural cascade that actually triggered the purchase.
Harvard research suggests that 95% of purchasing decisions happen subconsciously—driven by systems in the brain that customers can't access through introspection and wouldn't articulate even if they could.
This is the say-do gap, and it's why traditional marketing research keeps failing you.
You run surveys. You conduct interviews. You A/B test headlines. And still, the campaigns that should work... don't. The messaging that tested well... falls flat. The product features customers said they wanted sit unused.
Consumer neuroscience emerged to solve this problem. Instead of asking people what they think, neuromarketing measures what their brains and bodies actually do when exposed to marketing stimuli. It bypasses the unreliable narrator of conscious thought and goes straight to the source: physiological signals, neural activity, and behavioral patterns that reveal true preferences, attention, and emotion.
The neuromarketing market was valued at $3.3 billion in 2023 and continues to grow as more companies realize that understanding the why behind customer behavior isn't optional anymore—it's the competitive edge.
This isn't about installing an fMRI machine in your office. It's about understanding which techniques reveal what, how they're applied in practice, and where the ethical lines sit. Because if you're still guessing what your customers want based on what they tell you, you're operating with incomplete data.
And incomplete data leads to expensive mistakes.

The Marketer's Toolkit for the Subconscious Mind
At The Way How, we believe that understanding human behavior is the bedrock of effective marketing. This is where neuromarketing techniques truly shine. Unlike traditional marketing research, which relies on conscious self-reporting, neuromarketing digs into the subconscious, providing objective data on how consumers really react to marketing stimuli. This allows us to move beyond assumptions and diagnose the true drivers of stalled growth.
Neuromarketing employs a range of sophisticated tools to capture biometric data, physiological responses, brain activity, and behavioral tracking. These tools help us interpret the subtle, often unconscious, signals consumers send when interacting with your brand, products, or advertisements.
Here’s a snapshot of how neuromarketing research differs from traditional methods:
| Feature | Traditional Marketing Research | Neuromarketing Research |
|---|---|---|
| Methods | Surveys, focus groups, interviews, questionnaires | fMRI, EEG, eye-tracking, facial coding, GSR, heart rate |
| Data Type | Self-reported (conscious opinions, beliefs, stated preferences) | Objective (subconscious brain activity, physiological responses, involuntary behaviors) |
| Insights | What consumers say they think or want | What consumers actually feel, attend to, and are emotionally engaged by |
| Bias Susceptibility | High (social desirability, recall bias, conscious filtering) | Low (direct measurement of involuntary responses) |
Measuring Brain Activity
When we talk about understanding the "why" behind consumer choices, measuring brain activity is perhaps the most direct approach. These neuromarketing techniques provide a window into the mind, revealing how different stimuli impact attention, emotion, and memory.
fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging): This technique measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow. When a brain area is more active, it requires more oxygen, and fMRI scanners pick up on these variations in blood oxygenation. This allows us to map which parts of the brain are engaged during exposure to marketing messages. fMRI is excellent for its high spatial resolution, showing where activity occurs, making it valuable for understanding emotional engagement and memorization.
A classic example involved serving Coca-Cola and Pepsi to subjects in an fMRI machine. When the drinks were unidentified, neural responses were consistent. But when brands were visible, the parts of the brain associated with emotions, memories, and unconscious processing showed improved activity, highlighting the powerful influence of brand perception over mere taste.
- EEG (Electroencephalogram): While fMRI shows where brain activity happens, EEG excels at showing when. This technique measures the electrical activity of the brain through electrodes placed on the scalp. EEG provides excellent temporal resolution, meaning it can detect rapid changes in brain activity down to milliseconds. This makes it ideal for evaluating how marketing stimuli impact attention, engagement, and cognitive load in real-time. We can use EEG to understand how quickly an advertisement captures attention, how much mental effort is expended, or the emotional valence (positive or negative) evoked by specific elements. As the Mayo Clinic explains, EEG records electrical signals, creating wave patterns that reveal different brain states.
Tracking Physiological and Behavioral Responses
Beyond direct brain activity, our bodies and observable behaviors offer rich insights into subconscious reactions. These neuromarketing techniques provide complementary data, painting a more complete picture of the consumer experience.
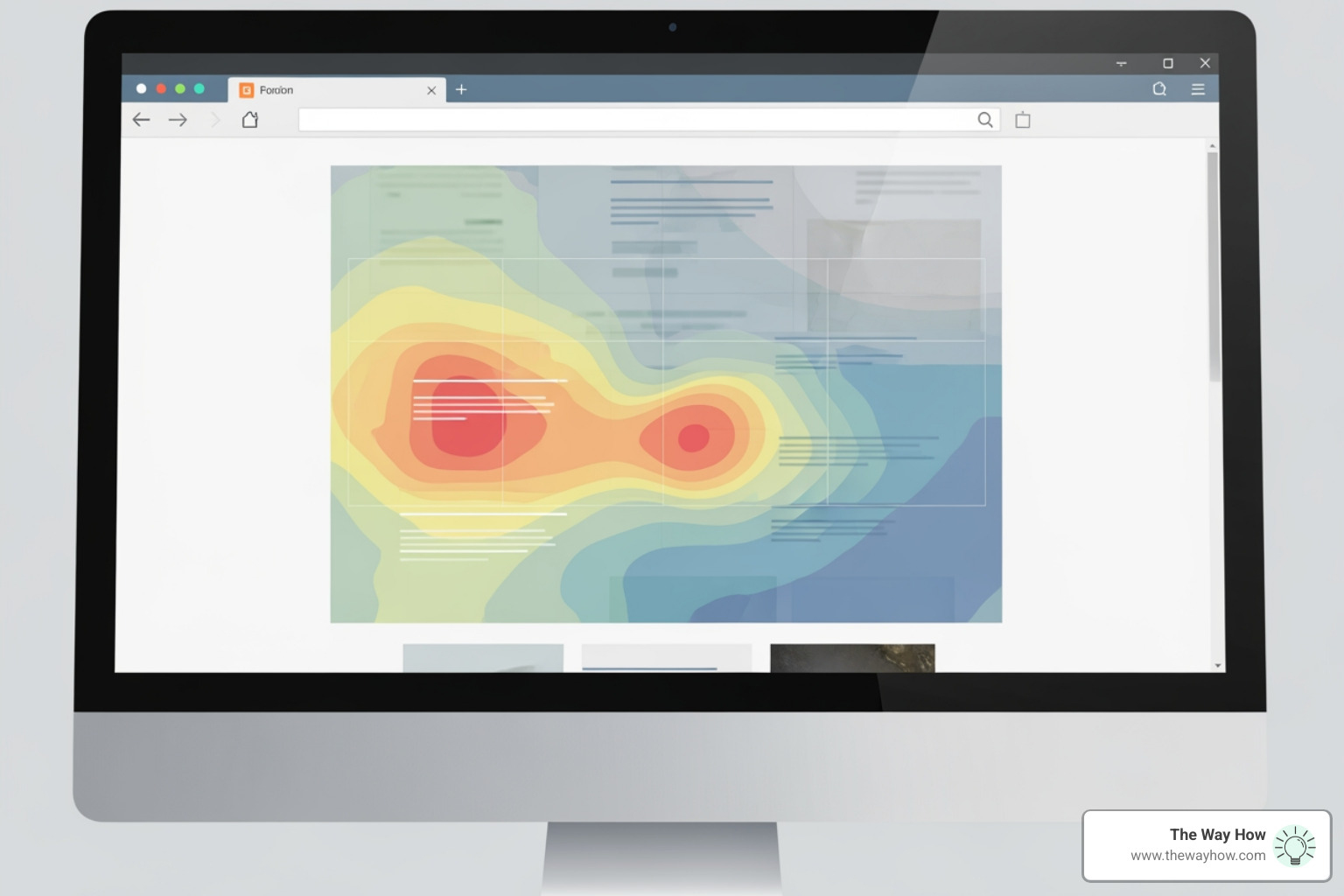
- Eye-Tracking: This technology records and analyzes where a person is looking, their gaze patterns, and pupil movements. It allows us to determine what elements on a webpage, advertisement, or product packaging capture visual attention, how long that attention is held, and the order in which information is processed. Heat maps generated from eye-tracking data visually represent areas of high attention, while gaze paths show the journey of a consumer's eyes, revealing cognitive processing. This helps us optimize layouts for clarity and impact.
- Facial Coding: Our faces are incredibly expressive, often betraying micro-expressions that indicate underlying emotions even before we're consciously aware of them. Facial coding involves analyzing these subtle facial movements to infer emotional states like joy, surprise, anger, or confusion. While some sources debate its scientific validation, it offers an indirect, non-intrusive way to gauge emotional valence in response to marketing stimuli.
- Biometrics: This category includes a range of physiological measures that reflect emotional arousal and cognitive engagement.
- Galvanic Skin Response (GSR): Also known as electrodermal activity (EDA), GSR measures changes in skin conductivity caused by sweat gland activity. Increased sweating, even imperceptible, indicates heightened emotional arousal or cognitive effort. It's a sensitive indicator of emotional impact.
- Heart Rate (HR): Changes in heart rate can signal attention, emotional intensity, or cognitive workload. For instance, heart rate deceleration often indicates increased attention, while an liftd heart rate can suggest excitement or stress.
By combining these diverse neuromarketing techniques, we gain a comprehensive understanding of how consumers truly experience marketing, moving past conscious narratives to the deeper, subconscious drivers of their decisions. This multi-faceted approach is crucial for diagnosing certainty gaps in the customer journey and building trust through truly empathetic design.
From Lab to Landing Page: Applying Neuromarketing Techniques in Your Strategy
The real power of neuromarketing techniques isn't just in understanding the brain; it's in translating those insights into actionable strategies that drive predictable revenue. This means applying what we learn from the lab to real-world marketing stimuli, refining the customer journey, optimizing conversion rates, and even informing A/B testing with a deeper understanding of human behavior. With the neuromarketing market valued at nearly $3.3 billion in 2023, businesses are clearly investing in these powerful methods to gain an edge.
Branding and Advertising That Resonates
How do we create brands and advertisements that don't just get noticed, but truly connect with consumers on an emotional, subconscious level? Neuromarketing techniques provide the answers.

- Logo Design: A logo is often the first interaction a consumer has with your brand. Neuromarketing research has shown how subtle elements can influence perception. For example, the FedEx logo includes a hidden arrow that subconsciously represents speed and efficiency, garnering favorable reactions and building trust.
- Color Psychology: Colors evoke powerful subconscious associations. Through brain activity research, we know that red signifies strength and passion. This is why iconic brands like Coca-Cola, Target, and Netflix prominently feature red in their logos, leveraging its inherent emotional impact.
- Brand Recall and Emotional Connection: Neuromarketing helps us understand what makes a brand memorable and emotionally resonant. Storytelling, for instance, is incredibly powerful. Research indicates that 63% of users remember brands that tell stories, and the human brain operates with stories, retaining 70% of information through them. Utilizing audio-forward media like podcasts or voice-over videos can also significantly catch and maintain a person's interest more effectively than traditional video alone.
- Advertising Effectiveness: Neuromarketing can pre-test advertisements to ensure they trigger desired subconscious responses. The National Cancer Institute, for example, used fMRI scans to test anti-smoking commercials. They found that the ad which elicited the most favorable brain reactions in test groups correlated with a higher number of calls to a smoking cessation hotline, demonstrating the technique's predictive power.
Optimizing Digital Experiences and Website Design
In the digital field, every click, scroll, and interaction is an opportunity to understand and influence consumer behavior. Neuromarketing techniques are vital for creating user experiences (UX) and website designs that reduce friction and guide users effortlessly toward their goals.
- User Experience (UX) and Website Layout: We know that consumers make rapid, often unconscious, judgments about a website's trustworthiness and usability. Eye-tracking studies can reveal exactly how users steer a page, identifying elements that cause confusion or draw attention away from key messages. This allows us to optimize call-to-action (CTA) placements, streamline navigation, and ensure cognitive ease.
- Reducing Decision Fatigue: Too many choices or complex interfaces can lead to decision fatigue, causing users to abandon a task. Neuromarketing helps us identify points of friction and simplify the user journey. Think about IKEA's famously effective store layouts; designed with neuromarketing insights, they strategically guide customers through a curated experience, increasing the likelihood of purchases before they can exit. The same principles apply to digital spaces: guiding users through a clear, intuitive path.
Product and Packaging Design Based on Applied Neuromarketing Techniques
The physical interaction with a product, from its packaging to its tactile feel, is a sensory experience that profoundly influences perception and purchase decisions. Neuromarketing techniques help us design products and packaging that appeal to these subconscious sensory preferences.
- Sensory Marketing and Product Aesthetics: Beyond visual appeal, how a product feels, smells, or even sounds can trigger powerful subconscious responses. Sensory words in copywriting, for example, activate the somatosensory cortex, making readers feel as if they are experiencing the product directly.
- Packaging Design: Packaging isn't just about protection; it's a silent salesperson. Through neuromarketing, Frito-Lay learned that matte bags with pictures of potatoes did not trigger a negative consumer response, unlike shiny bags with pictures. This insight led them to change their chip packaging, demonstrating how subtle design elements can significantly impact consumer preference.
- The Influence of Price Perception: Price is often perceived as an indicator of quality, even when the product is identical. A fascinating study at INSEAD scanned the brains of test subjects while they tasted three wines, each labeled with a different price. Their brains registered the wines differently, with neural signatures indicating a preference for the most expensive wine—even though all three wines were, in fact, the same. This illustrates how price can alter the subjective experience and activate reward pathways.
By understanding these deep-seated psychological and neurological responses, we can design marketing strategies that are not just theoretically sound but are empirically proven to resonate with the human mind.
The Double-Edged Sword: Benefits and Ethical Lines
As with any powerful tool, neuromarketing techniques come with both significant advantages and crucial ethical considerations. For businesses, the benefits can be transformative, offering unprecedented insights into consumer behavior. However, this power also demands a strong commitment to ethical practice.
The Business Benefits of Understanding the 'Why'
When we move beyond surface-level data and into the subconscious drivers of consumer behavior, businesses open up a host of advantages:
- Improved Customer Understanding: Neuromarketing provides a granular view of how customers process information, react emotionally, and form memories related to your brand. This deeper understanding allows for truly customer-centric strategies, building empathy into every touchpoint.
- Increased Marketing Effectiveness: By understanding subconscious triggers, we can craft more persuasive and engaging marketing messages. Studies suggest that neurological engagement can increase advertising effectiveness by up to 19%. This translates directly into campaigns that resonate more deeply and convert more efficiently.
- Reduced Waste in Ad Spend: Testing marketing stimuli with neuromarketing tools before a full campaign launch allows us to identify ineffective elements and optimize successful ones. This precision minimizes the risk of costly failures, ensuring marketing budgets are spent on strategies that truly work.
- Increased Customer Loyalty: When products and marketing messages align with consumers' true desires and emotional needs, the connection becomes stronger. This leads to more loyal customers who feel understood and valued, reducing churn and fostering long-term relationships.
- Better Product Development: Insights from neuromarketing can guide product design and features, ensuring that what you offer truly appeals to your target audience. It helps create products that aren't just functional but also emotionally satisfying.
Navigating the Ethical Considerations of Neuromarketing Techniques
The ability to peer into the subconscious mind raises important questions about manipulation versus persuasion. Our approach at The Way How is rooted in empathy and clarity, never exploitation.
- Transparency and Informed Consent: Ethical neuromarketing absolutely requires transparency with participants. Individuals involved in studies must give informed consent, understanding what data is being collected and how it will be used.
- The "Buy Button" Myth: While neuromarketing offers powerful insights, it's crucial to dispel the myth of a magical "buy button" in the brain that can be simply pressed. Consumer decision-making is complex, influenced by a multitude of factors, and neuromarketing techniques provide insights, not mind control. The goal is to create products and experiences that genuinely meet needs and desires, not to coerce purchases.
- Potential for Misuse: The power of neuromarketing means there's a potential for misuse, particularly if insights are used to exploit consumer vulnerabilities rather than serve their needs. For example, a political party in Mexico used neuromarketing to understand voters' reactions to campaign ads. When this information leaked, it caused significant public backlash, demonstrating the ethical tightrope involved.
- Industry Codes of Conduct: Reputable neuromarketing firms and researchers adhere to strict ethical guidelines and industry codes of conduct to ensure responsible data collection, analysis, and application of insights. Our focus is always on understanding to better serve, not to manipulate.
Frequently Asked Questions about Neuromarketing
How is neuromarketing different from traditional marketing?
Traditional marketing primarily relies on self-reported data, such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups. These methods capture conscious opinions and beliefs, but they are susceptible to biases like social desirability (people saying what they think they should say) or an inability to articulate subconscious motivations.
Neuromarketing techniques, on the other hand, employ neuroscientific tools to measure objective, unfiltered physiological and neural responses. This includes brain activity (fMRI, EEG), eye movements (eye-tracking), facial micro-expressions (facial coding), and other biometric data (GSR, heart rate). These tools reveal what consumers truly feel, attend to, and are emotionally engaged by, bridging the "say-do gap" between what they consciously report and what their brains and bodies actually indicate. It provides a more accurate and holistic understanding of consumer decision-making processes, which are largely driven by unconscious factors.
Is neuromarketing too expensive for small businesses?
While high-end tools like fMRI machines are indeed costly and typically reserved for large corporations or specialized research institutions, the field of neuromarketing is becoming more accessible. Many neuromarketing techniques are now available through more affordable and portable solutions. For instance:
- Wearable EEG devices and simpler eye-tracking software have significantly reduced costs.
- AI-powered platforms can analyze facial coding data from standard webcams or process eye-tracking data more efficiently, making these techniques more scalable and less expensive.
- Furthermore, applying the principles derived from neuromarketing research often doesn't require direct access to the equipment. Understanding how color psychology, storytelling, or loss aversion influences behavior can be implemented in copywriting, design, and strategy without a lab. Our expertise at The Way How lies in translating these complex insights into practical, implementable strategies that fit various budgets.
Can neuromarketing be used to manipulate people?
This is a critical and frequently asked question, touching on the core ethical debate surrounding neuromarketing techniques. While neuromarketing undeniably provides powerful insights into subconscious drivers and emotional triggers, its ethical application focuses on creating better, more relevant experiences for consumers, not forcing them into unwanted purchases.
We believe that responsible neuromarketing is about understanding human behavior to:
- Reduce friction: Making products and services easier and more intuitive to use.
- Improve value: Designing offerings that genuinely resonate with consumer needs and desires.
- Improve communication: Crafting messages that are clear, empathetic, and truly connect with the audience.
The goal is to build trust and foster genuine connections, leading to predictable revenue through authentic engagement. Manipulation, by contrast, seeks to exploit vulnerabilities for short-term gain, which ultimately erodes trust and damages long-term brand equity. Ethical guidelines and industry standards exist to prevent misuse, emphasizing informed consent, data privacy, and a commitment to improving the customer experience rather than exploiting it.
Building Certainty in an Uncertain World
In a world brimming with marketing noise and fleeting trends, understanding the fundamental drivers of human behavior is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity. At The Way How, we recognize that true marketing and revenue strategy is psychology-first. We diagnose why growth is stalled not by guessing, but by employing a systematic approach rooted in human behavior, empathy, and decision-making psychology.
Neuromarketing techniques represent a powerful frontier in this endeavor. By illuminating the subconscious pathways that guide consumer choices, they help us remove uncertainty in your sales and marketing systems. This isn't about chasing tactics; it's about identifying certainty gaps in the customer journey and designing systems that create trust, momentum, and predictable revenue.
The future of marketing will increasingly blend strategic clarity with behavioral insight and operational execution. As AI continues to advance, it will further democratize access to neuromarketing insights, making scalable insights available to more businesses.
If you're ready to move beyond the guesswork and build a dependable growth engine grounded in a deep understanding of your customers, we're here to help. Find more info about our services and let us help you achieve clarity in your marketing strategy.
Want to Learn Something Else?